Public Cloud vs Private Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud: Which One is Right for You?
By 2025, over 200 zettabytes of data will be stored in the cloud, more than half of the world’s total data. The shift isn’t coming, it’s already here. But storing data is just one part of the equation.
The bigger question for most businesses now is: What kind of cloud setup makes sense for us? Public cloud looks cost-effective, private cloud offers control, and hybrid cloud tries to bring the best of both. But the real answer depends on what your business values most—speed, security, budget, or flexibility.
This blog breaks down each model, not to sell you one, but to help you pick what actually fits.
Quick Comparison: Public Cloud vs Private Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud
| Cloud Model | Ownership | Resources | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public | Third-party provider | Shared (multi-tenant) | Scalability, cost-effectiveness, remote teams, standard workloads | Pay-as-you-go, wide services, managed by provider, easy scaling |
| Private | Single organization/on-prem or host | Dedicated to one org | Sensitive data, compliance, strict security, maximum customization | Full control, high security, custom setup, higher cost |
| Hybrid | Mix of public + private | Combination of both | Businesses needing flexibility, compliance, load balancing | Keeps critical data private, uses public for scale, flexible |
Why Is Cloud Computing Essential For Modern Businesses?
Cloud computing has become a key part of how modern businesses work and grow. It helps companies manage data, run applications, and support daily operations without needing heavy IT infrastructure. Whether it’s a startup or a large organisation, cloud services allow faster setup, lower upfront costs, and easier access to tools and storage.
As teams grow and work becomes more distributed, cloud computing also brings better collaboration, flexibility, and speed. It supports data backup, system updates, and security without much manual effort. Instead of relying on in-house servers, businesses can stay focused on goals while the cloud takes care of the backend.
But not all cloud setups work the same way. It’s important to understand how different cloud deployment models function before deciding what fits best.
Understanding Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud deployment models define how computing resources are implemented and accessed. The three primary models are public, private, and hybrid clouds, each offering distinct advantages based on an organization’s needs regarding scalability, security, and cost.
Each model brings its own strengths; let’s break down what each type of cloud means for your business.
What Is A Public Cloud?

A public cloud is a type of cloud computing where services such as storage, virtual machines, and databases are provided by third-party services like AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure. These services operate on shared infrastructure, but users’ data and workloads are distinct and safe. All of this, from setup to maintenance, is handled by the provider, so companies don’t have to worry about hardware, updates, or security patches.
The pay-as-you-go model keeps it affordable, particularly for startups or businesses with variable workloads. Public cloud is suitable for testing environments, application hosting, backup management, or remote teams support. Scaling up or down is simple based on usage, which makes it perfect for businesses that move fast and require flexibility without the cost of infrastructure management.
Advantages Of Public Cloud
- Budget-friendly setup
Public cloud removes the need to buy, install, or maintain physical servers. This reduces upfront costs significantly for small and mid-sized businesses that need reliable infrastructure without heavy investment. - Grows with your business
Whether you’re onboarding new users or expecting traffic surges, public cloud resources can scale automatically. As per Gartner, global spending on public cloud is expected to hit $675 billion in 2024, showing how widely it’s being adopted. - Remote access from anywhere
With just an internet connection, teams can access business tools, files, and applications on the go. It’s a major plus for businesses working remotely or across multiple locations. - Disaster recovery built-in
Public cloud platforms usually include quick backup and recovery options. In case of server failure or cyberattacks, businesses can restore operations in minimal time without added setup. - Faster global expansion
Public cloud lets you launch services across different countries without setting up local infrastructure. This makes it easier for growing businesses to reach users worldwide.
Up next, let’s talk about where public clouds may not work as smoothly.
Disadvantages Of Public Cloud
- Less control over data
Your data lives on third-party infrastructure, which means less transparency and direct access concerning industries with strict compliance needs. - Inconsistent performance at times
Since you’re sharing infrastructure with others, performance may drop during high-traffic periods. For applications needing consistent speed, this can be a concern. - Security is shared
Providers do follow best practices, but being on shared servers might still make businesses uneasy, especially when handling financial or personal data. - Customer support isn’t always prompt
Basic support plans might leave businesses waiting. Faster or more personalized support often comes with premium pricing.
Long-term costs can rise
Although it’s affordable at first, ongoing usage, storage upgrades, or outbound data transfer can quietly increase monthly bills if not monitored closely.
For more details, see our guide on the pros and cons of cloud computing.
What Is A Hybrid Cloud?
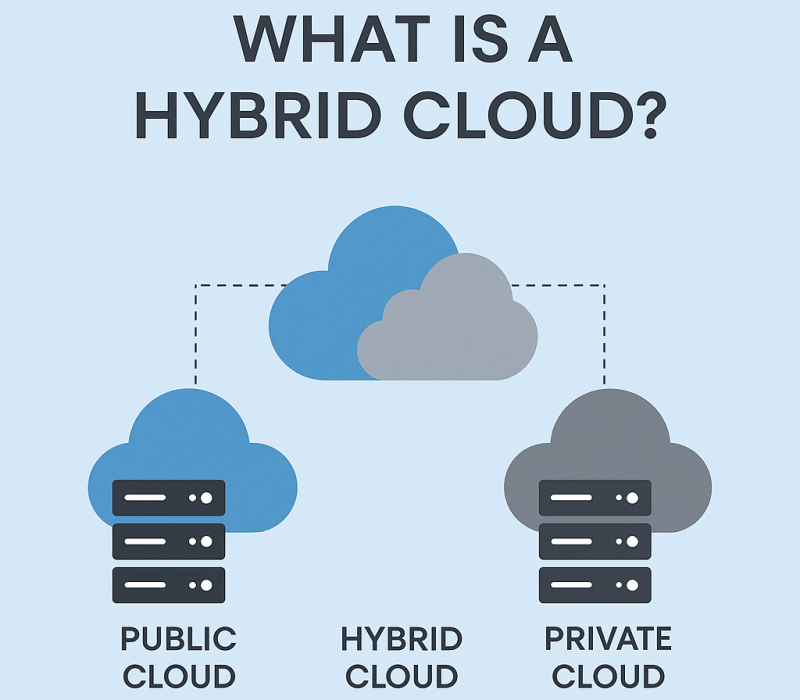
Hybrid cloud is a setup where businesses use both public and private cloud systems together. It allows you to maintain sensitive or critical data in a private environment, with the day-to-day tasks such as file storage, development, or application usage in the public cloud. The two platforms work together so that you have the ability to move data or workloads back and forth, depending on what’s needed.
It’s useful for companies that need more security in some areas but still want the flexibility and cost benefits of public cloud. Many use it to manage traffic spikes, keep customer data secure, or meet strict compliance rules without giving up performance or scale.
Now, let’s look at the advantages and disadvantages of the hybrid cloud so you can weigh whether it’s the right fit for your business.
Advantages Of Hybrid Cloud
- More control over critical data
Hybrid cloud allows businesses to keep sensitive data on private servers while using the public cloud for general operations, offering better control without compromising accessibility or performance. - Cost optimization for varied workloads
According to Flexera’s 2024 State of the Cloud report, 72% of companies say hybrid models helped cut costs by letting them avoid overpaying for underused infrastructure. - Reliable disaster recovery and uptime
In case of a system failure, hybrid environments automatically shift operations between public and private setups, minimizing downtime and protecting against data loss without needing additional backup tools. - Faster development and deployment cycles
Teams can test, develop, and launch applications quickly using public cloud tools while keeping production workloads secure in a private environment, cutting delays often caused by limited in-house resources. - Supports regulatory compliance
Businesses in healthcare, finance, or government can run compliance-sensitive workloads privately while using the public cloud for regular operations, meeting data regulations without losing cloud flexibility.
Disadvantages Of Hybrid Cloud
- Complex to maintain and secure
Managing both cloud types takes technical expertise, especially when handling data transfers, ensuring security, and preventing inconsistencies between the two environments. - Integration challenges with legacy systems
Older on-premise setups don’t always work smoothly with modern cloud platforms, which can result in performance bottlenecks or the need for additional middleware. - Initial setup is time-consuming
Planning a hybrid environment means setting clear policies for workloads, access, and storage. This adds complexity in the early phase and can delay migration timelines. - Risk of misconfigurations
Without strict access controls or proper network monitoring, hybrid environments can expose sensitive data during transitions when teams lack experience with multi-platform setups.
Learn how hybrid models can address key cloud migration challenges faced by growing businesses.
What Is A Private Cloud?

Private cloud adoption continues to grow, with 84% of companies now using at least one private cloud setup in their stack. That says a lot about how essential it’s become for businesses handling sensitive data or complex workflows.
A private cloud is a dedicated environment built for a single organization, where the infrastructure is not shared with others. It can be set up on-premises or hosted by a trusted third-party provider. Unlike public cloud, private cloud gives full control over data, access, and security policies, making it a preferred option for businesses that deal with sensitive data. Industries such as finance, healthcare, and legal often rely on this model to meet strict compliance needs.
It offers better visibility and governance over critical workloads while maintaining the flexibility of cloud infrastructure.
Advantages Of Private Cloud
Private Cloud offers several unique advantages for businesses that prioritise control, compliance, and data security:
- Control over infrastructure
Private Cloud gives you full control over how infrastructure is configured, monitored, and maintained, an important factor for organisations with strict internal processes or legacy system dependencies. - Security for sensitive workloads
When hosted internally or with a trusted third-party provider, Private Cloud significantly reduces external threats and also Private clouds integrate seamlessly with cybersecurity solutions to meet strict compliance requirements.. This setup is often preferred in finance, healthcare, or government sectors where data protection is non-negotiable. - Compliance-ready environment
Industries bound by regulations like HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or GDPR often choose Private Cloud to ensure strict compliance without compromise. Audits and reporting are easier when systems are centralised and under direct control. - Predictable performance
Unlike public environments where resources are shared, Private Cloud ensures dedicated computing and storage power, which results in more predictable workloads and consistent application performance. - Flexible hosting options
Many businesses rent hardware or opt for hosted private setups to avoid large upfront costs. It’s not always about on-premises servers. Service providers now offer flexible, scalable private cloud infrastructure, too.
Disadvantages Of Private Cloud
Despite its benefits, Private Cloud comes with a few critical drawbacks that businesses must weigh carefully:
- High capital and maintenance costs
Setting up a Private Cloud involves upfront investment in hardware, licenses, and skilled IT personnel. Ongoing maintenance also demands time, cost, and dedicated resources, especially for updates and security management. - Scalability limitations
Scaling private infrastructure isn’t as quick or cost-effective as Public Cloud. If demand spikes unexpectedly, provisioning additional resources can take time and often involves complex procurement and setup processes. - Resource dependency
Running a Private Cloud means relying heavily on in-house teams. Downtime, misconfigurations, or skill gaps can slow down operations in smaller businesses without a large IT staff. - Longer deployment cycles
Deploying new applications or environments often takes longer on Private Cloud due to manual configurations and capacity planning. It’s not ideal if speed-to-market is a major business priority.Limited PaaS and integrations
Unlike Public Cloud, Private environments may lack access to a wide variety of platform services, third-party integrations, or AI tools unless you build them in-house or pay extra for them.
Key Differences Between Public, Private, And Hybrid Cloud
Knowing how Public, Private, and Hybrid clouds differ helps in choosing what best fits your business. The table below breaks down the key differences across areas like cost, security, performance, and scalability.
Feature | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | HybridC loud |
Cost | Pay-as-you-go model, lower upfront costs, but expenses may rise with usage. | Higher setup costs, but more predictable long-term expenses. | Mix of both predictable for critical systems, flexible for fluctuating workloads. |
Security | Secure, but shared infrastructure may not suit all compliance requirements. | Dedicated environment with tighter control over data and access. | Sensitive data stays private, while non-critical data uses public resources securely. |
Performance | Can vary depending on demand and network conditions. | Stable and consistent performance due to dedicated resources. | Balances both critical apps run privately, less critical ones scale on demand. |
Scalability | Highly scalable, can adjust quickly to workload changes. | Scalable, but scaling requires more planning and investment. | Scales flexibly across environments, depending on need and budget |
Compliance | May not support specific industry regulations. | Ideal for businesses with strict compliance needs like HIPAA or PCI-DSS. | elps maintain compliance for sensitive workloads while optimising for cost and efficiency elsewhere. |
Customisation | Limited standardised infrastructure and services. | Fully customisable to meet performance, security, and policy requirements. | Allows custom configurations on private side while using public for standardised operations. |
Which Model Should You Choose?

Choosing between public, private, and hybrid cloud isn’t about what’s better. If your team lacks in-house expertise, managed IT services can simplify public or hybrid cloud adoption. It’s about what fits your setup best. Start with these questions:
- What are you prioritising right now?
If cost control or quick scaling is the main focus, public cloud usually works well. No hardware hassles, just pay for what you use. - How sensitive is your data?
Private cloud gives you more control. Good for teams handling personal records, financial data, or anything that’s under strict compliance rules. - Do you need both flexibility and security?
A hybrid cloud can help you split your workload smartly, public cloud for the less sensitive stuff and private for what needs protection. - Is your team equipped to manage infrastructure?
If you don’t have a strong IT team, managing a private cloud could become a full-time headache. Public or hybrid options are easier to maintain. - How steady are your workloads?
If your app usage is unpredictable, public cloud’s scalability might help you avoid overpaying. But if things stay stable, private cloud can offer more consistency.
Still not sure? It’s okay. A quick talk with someone who’s done it before can save you time, money, and future headaches. Better to ask early than fix later.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the main difference between public, private, and hybrid cloud?
A: Public cloud shares resources via third-party providers, private cloud is a dedicated environment for one organization, and hybrid cloud combines both for flexibility and control.
Q2: Which cloud model is most secure for business data?
A: Private cloud typically offers the highest security due to dedicated resources and custom controls, but hybrid cloud allows sensitive data to stay private while other tasks use the public cloud.
Q3: Is hybrid cloud more expensive than public cloud?
A: Hybrid cloud can cost more than public cloud alone due to the need to manage both environments, but it lets you balance costs by only keeping mission-critical or sensitive workloads private.
Q4: How do Australian regulations affect cloud choice?
A: Australian businesses should consider the Privacy Act and industry compliance requirements—private or hybrid clouds may be required for strict data residency or sensitive sectors.
Q5: Can I switch from public to hybrid cloud later?
A: Yes. Many businesses start in public cloud for cost and scale, then move critical workloads to a private or hybrid setup as security or compliance needs grow.
Q6: What are the best use cases for each cloud model?
A: Public cloud suits startups, fast scalability, and general apps; private cloud is best for finance, healthcare, and compliance-heavy industries; hybrid cloud is ideal for organizations needing flexibility and data segregation.
Conclusion
There’s no one-size-fits-all when it comes to cloud solutions. The right choice depends on what your business values most: cost-efficiency, control, or a balance of both. Public Cloud is great for businesses needing fast scalability without high upfront costs. Private Cloud fits companies with sensitive data and strict compliance needs. Hybrid Cloud works well when you want flexibility without giving up control.
Before making the move, it’s worth mapping your workload needs and long-term goals. If you’re still unsure, working with trusted cloud experts like Hyetech can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your business priorities.
